Simple and best practice solution for F(x)=(x1)(x3) equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, soIf x not =3 5 ;if x=3 Show that f(x) is continuous at x=3 Share with your friendsThe difference quotient is given by $$$ \frac{f{\left(x h \right)} f{\left(x \right)}}{h} $$$ To find $$$ f{\left(x h \right)} $$$, plug $$$ x h $$$ instead
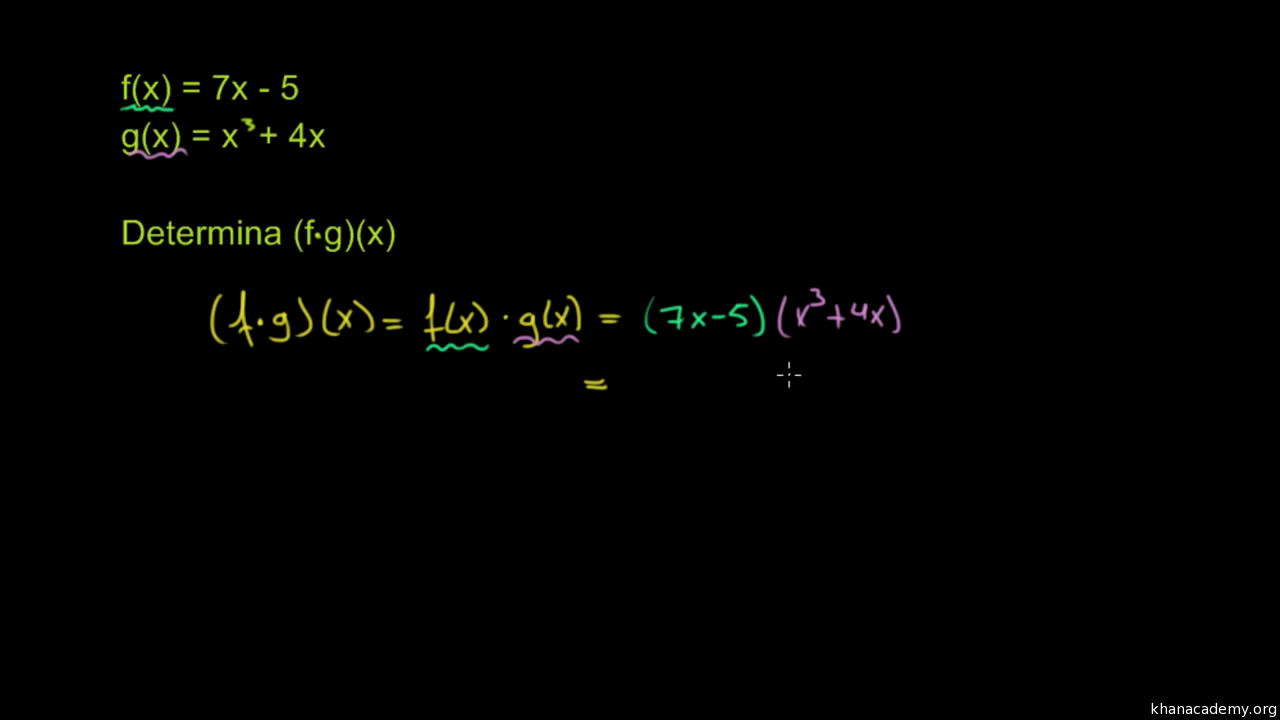
Multiplicar Funciones Video Funciones Khan Academy
F(x)=x^3-4x
F(x)=x^3-4x-Given the function f (x) as defined above, evaluate the function at the following values x = –1, x = 3, and x = 1 This function comes in pieces;Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge and




Given That F X 2 X 4 And G X 3 X 5 Find Gf 3 With Noob Like Steps Please I Need A Really Clear Working To Fully Understand Thanks 3 Socratic
Mar 17, 14 · A function f(x) is defined as , f(x)={(x 2x6)/x3;Sep 12, · If f(x) = 1 – x x2 – x3 –x99 x100, then f'(1) is equal to A 150 B –50 C –150 D 50 Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queriesAs we saw in the example of f (x) = x 3, f (x) = x 3, a function fails to be differentiable at a point where there is a vertical tangent line As we saw with f (x) = {x sin (1 x) if x ≠ 0 0 if x = 0 f (x) = {x sin (1 x) if x ≠ 0 0 if x = 0 a function may fail to be differentiable at a point in
We can rewrite f (x) as , f (x) = x3 for x ≥3 = 3x for x < 3 LHL of f (x) at x=3 is 0 RHL of f (x) at x=3 is 0 So, f (x) is continuous at x=3 RHD of f (x) at x=3 , limh→0 { 3h−3(3h)−3−(3−3)==> f' (x) = The stationary points are where f' (x) isShort Solution Steps f ( x ) = x ^ { 3 } ( 1 \frac { 4 } { x 6 } ) f ( x) = x 3 ( 1 − x 6 4 ) To add or subtract expressions, expand them to make their denominators the same Multiply 1 times \frac {x6} {x6} To add or subtract expressions, expand them to make their denominators the same
Mar 09, 18 · Explanation the denominator of f (x) cannot be zero as this would make f (x) undefined Equating the denominator to zero and solving gives the value that x cannot be solve x −3 = 0 ⇒ x = 3 ← excluded value domain is x ∈ R,x ≠ 3 ( − ∞,3) ∪(3, ∞) ← in interval notationF(x) = x 3 9x g(x) = x 2 2x 3 f(x)/g(x) = (x 3 9x) / (x 2 2x 3) The denominator, x 2 2x 3 is a quadratic equation and can be simplified by factorization x 2 2x 3 = x 2 3x x 3 = (x 2 3x) ( x 3) = x(x 3) 1(x 3) = (x 3)(x 1) And the numerator, x 3 9x can also be simplified by facorization x 3 9x = x(x 2Apr 12, 16 · If x>3, which of the following is equivalent Magoosh SAT Source New SAT Study Guide Test 1;




Expand In Fourier Series F X X2 X 3 2 Wegglab




Misc 18 If F X X 3 Show That F X Exists And Find It
Graph f (x)=x3 f (x) = x − 3 f ( x) = x 3 Rewrite the function as an equation y = x− 3 y = x 3 Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is y = m x b y = m x b, where m m is the slope and b b is the yintercept y = m x b y = m xExample 1 Find a power series representation for f (x) = 1 1x and its domain We use the representation of 1 1 x, replacing x by x We obtain 1 1x = 1 1 ( x) = 1( x)( x)2 ( x)3 = 1 xx2 x3 = X1 n=0 ( 1) nx The series representation for 1 1 x was valid if jxj < 1 If we apply the same substitution, we see that thisGraph the exponential problem F(x)=3 x Hi Jose, Set up b and extend the table to x F(x) 1 3 1 = 3 2 3 2 = 9 3 3 3 = 271 31 = 1/32 32 = 1/93 33 = 1/27 Also 3
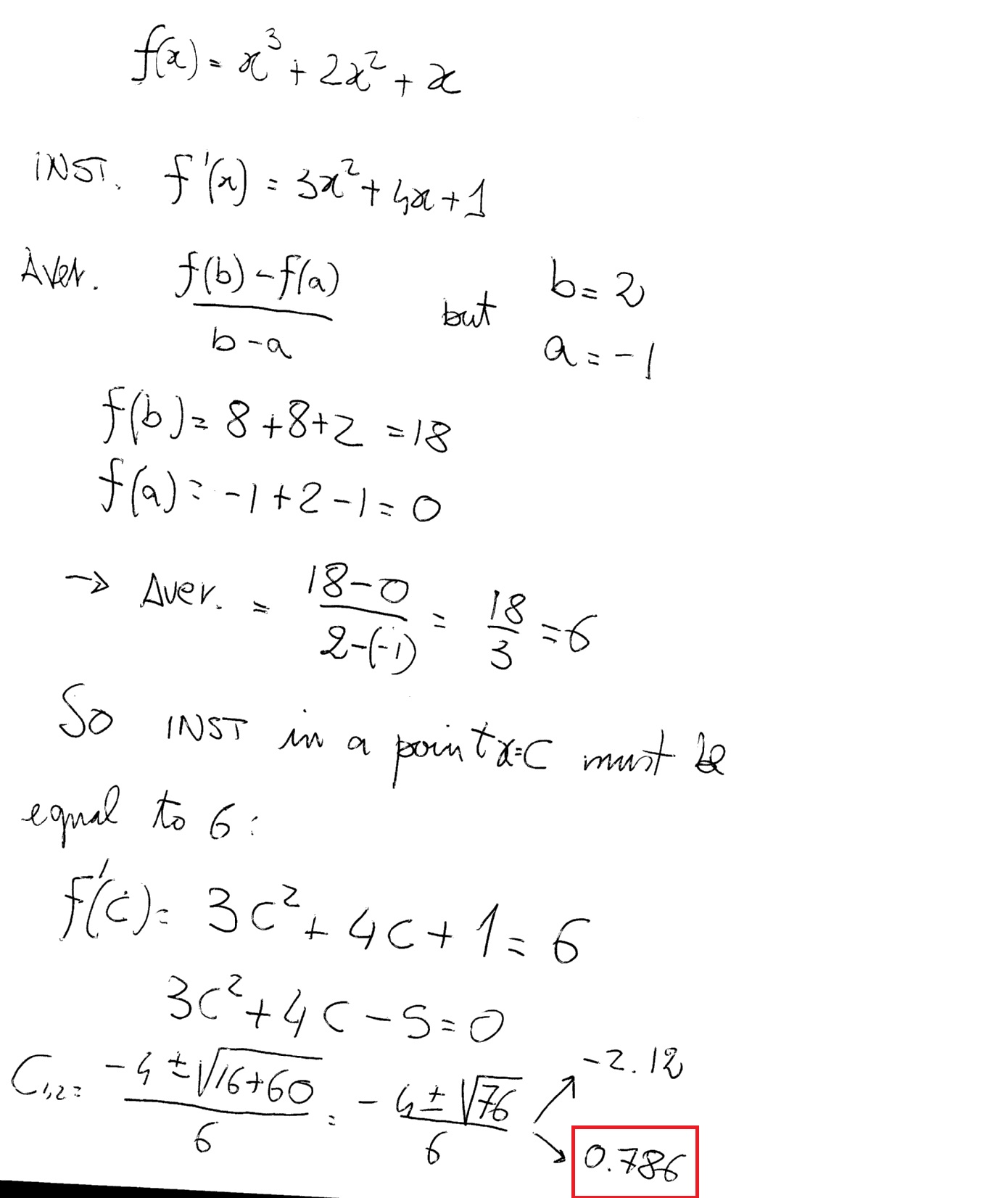



If F Is Defined By F X X 3 2x 2 X How Do You Find The Value Of X When The Average Rate Of Change Of F On The Interval X 1 To X




Derivadasaplicacion
F(x) = x 3 and g(x) = x2 − 2 (f g)(5) Answer by MathLover1() (Show Source) You can put this solution on YOUR website!So we have two x times off base You was, uh, X squared times three f squared off pecs terms E l x, The X that is equal zero since wrecked inside is just a constant So we are ready to know, like values in Were drunk went mental and form one plus two times f o Born Q plus warm times threeThe line $$$ x=L $$$ is a vertical asymptote of the function $$$ y=\frac{2 x^{3} 15 x^{2} 22 x 11}{x^{2} 8 x 15} $$$, if the limit of the function (onesided) at this point is infinite In other words, it means that possible points are points where the denominator equals $$$ 0 $$$ or doesn't exist So, find the points where the denominator equals $$$ 0 $$$ and check them




Example 8 Discuss Continuity Of F X X3 X2 1 Examples




Si F X 2x A X 3 Y F 2 0 Cual Es El Valor De A Donde No Esta Definida F Brainly Lat
Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!Apr 04, 21 · f (x) = 2x 4 − x 6 f ' (x) = a) Find the derivative of the function h ( x ) = 10 x12 6 x6 − 2 x3 19 x − 7 h' (x) = Expert Answer Who are the experts?Evaluate the function for and first find




If F 2 X F 1 X1 X X 3 X 1 1 F X 0 Then Find F 2 Where Is The G I F




Derivada De Un Producto F X X 2 X 3 Youtube
Apr 30, 18 · If f R → R is a function defined by f(x) = 3x – 2 1 Show that f is oneone 2 Find fof(x) 3 Find the inverse of f if existsProve that f R → R, f (x) = cos x is a many one into function Change the domain and co domain of f such that become Change the domain and co domain of f such that become One one ontoHence the slope of the graph of the square function at the point (3, 9) is 6, and so its derivative at x = 3 is f ′ (3) = 6 More generally, a similar computation shows that the derivative of the square function at x = a is f ′ (a) = 2a




Determine Las Derivadas De Las Siguientes Chegg Com
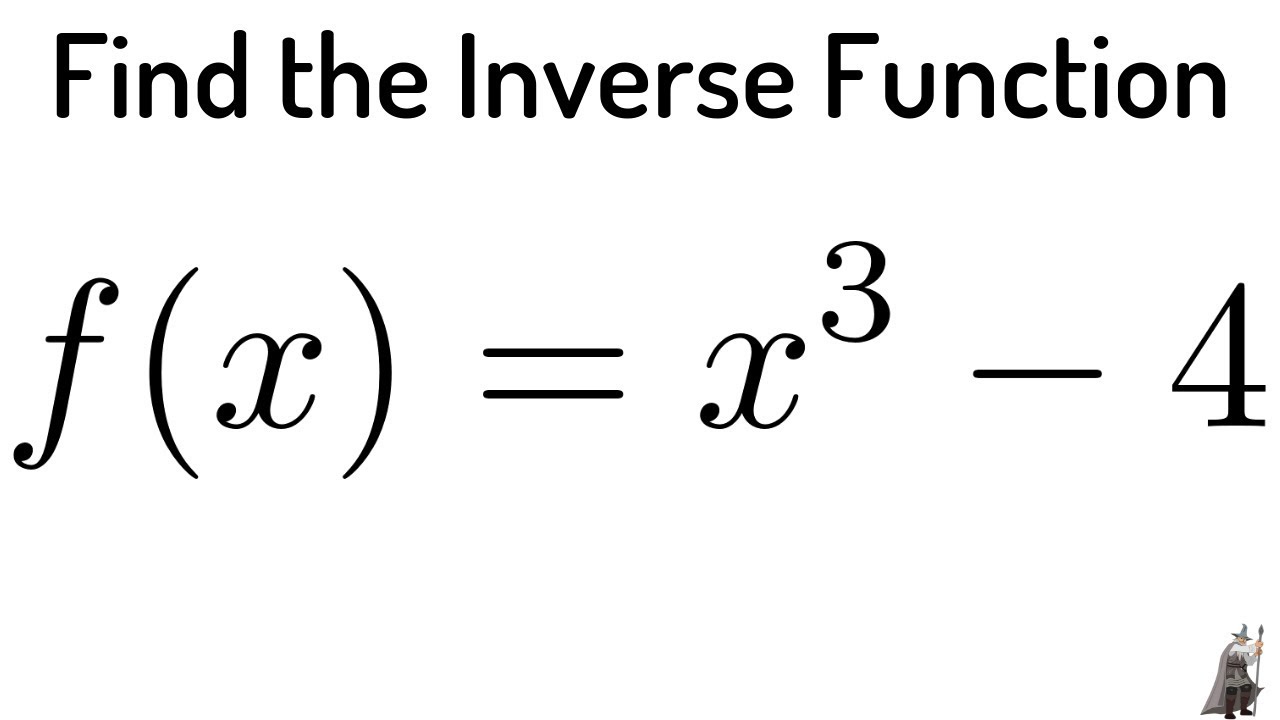



19 Find The Inverse Function For F X X 3 4 Youtube
Graph f (x)=3^x f (x) = 3x f ( x) = 3 x Exponential functions have a horizontal asymptote The equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = 0 y = 0 Horizontal Asymptote y = 0 y = 0Let mathf(x) = x^3 x/math I'm assuming that mathf\mathbb{R}\to \mathbb{R} /math Since mathf(x)/math is a bijection mapping (the proof is very simple and I hope you know that) Therefore its inverse exists uniquely For finding theMar 18, 21 · Like the Function f (x)=x^3 Tom McCoy returns to bamboozle us And over what?




Calameo Calculo De Derivadas I




Let F X X 3 3x 2 9x 2 Then F X Has A Maximum At X 1 B
3 Find the indicated derivative for each function Show your work (Sec 26) Find y000, y= 4x4 x2 7 Solution y0= 16x3 2x y00= 48x2 2 y000= 96x Find d2f dx2, where f(x) = xsinx Solution f0(x) = xcosx sinx f00(x) = cosx xsinx cosx= 2cosx xsinx Find r(4), where r(x) = 1=x Solution r0(x) = 1=x2 r00(x) = 2=x3 r000(x) = 6=x4 r(4)(x) = 24=x5 4 Find a tangent line through the curve 2x 2Write (10x2)(x 2) as 10*x2x^2 2 Write cos(x 3) as cos(x^3) 3 Write e x lnx as e^xln(x) 6 Ensure that the input string is as per the rules specified above An online derivative calculator that differentiates a given function with respect to a given variable by using analytical differentiation A useful mathematical differentiationF ( x ) = 3 x ^ { 3 } x 2 f ( x) = 3 x 3 − x 2 By Rational Root Theorem, all rational roots of a polynomial are in the form \frac {p} {q}, where p divides the constant term 2 and q divides the leading coefficient 3 One such root is 1 Factor the polynomial by dividing it by x1 Polynomial 3x^ {2}3x2 is not factored since it does not have any rational roots




1 F X X3 1 X F X X2 9 X F X X 3 X 2 X 3 X 1 F X 5 F X X 5 X F X X2 3 X 2 X 2 3 X Pdf Free Download




Calculo De Derivadas By Apolinar Pancho Espinar Issuu
Justify your answer f (x) = ((x − 2)/(x − 3)) Check oneone f (x1) = ((x"1 " − 2)/(x"1" − 3)) f (x2) = ((x"2 " − 2)/(x"2" − 3)) Putting f (x1) =A teacher at a secondary school in London reviews equations on a whiteboard Credit Peter Macdiarmid, via GettyThe function is F(x) = x 3 x 2 19x 14 At x= 500 F(x) is equal to 900 At x= 600 F(x) is equal to 50 Intuitively we feel, and justly so, that since F(x) is negative on one side of the interval, and positive on the other side then, somewhere inside this interval, F(x) is zero Procedure
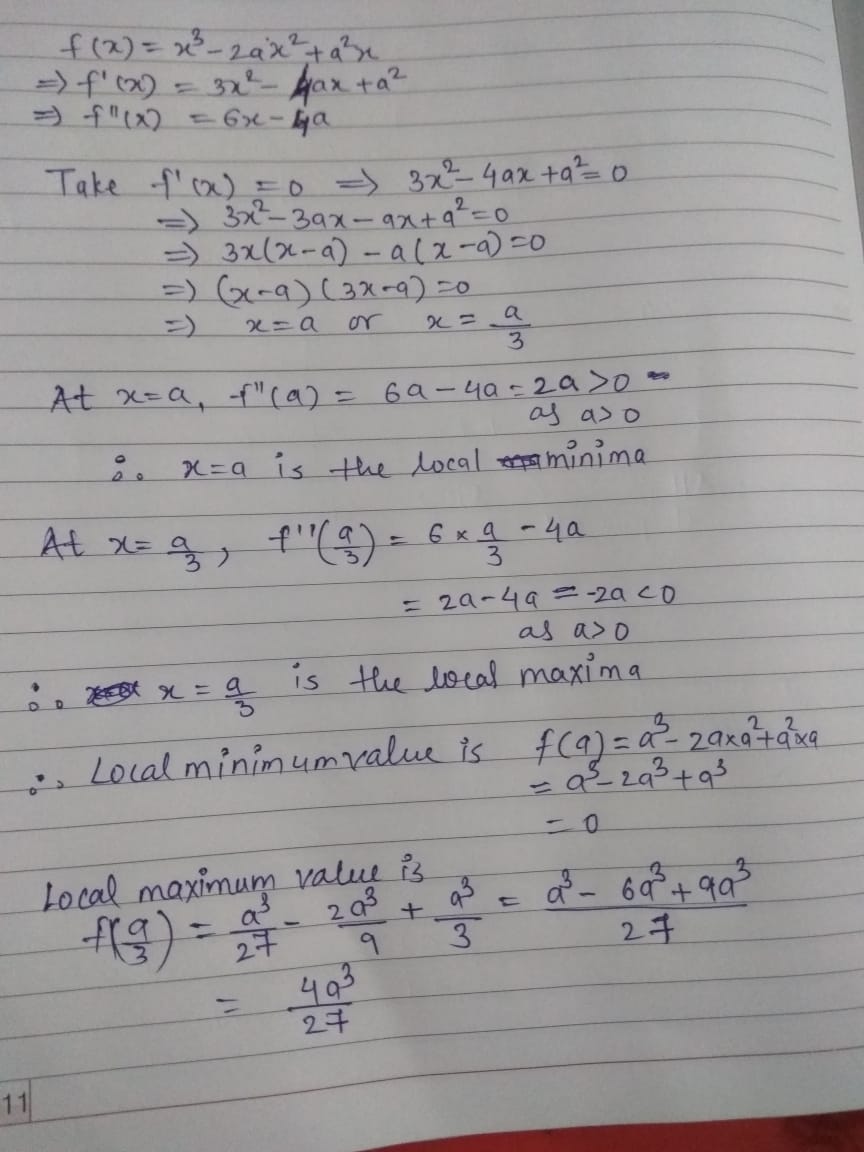



Fimd The Point Of Local Maxima And Local Minima And Corresponding Local Maxima And Local Minima Values Of Each Of The Following Funct F X X 3 2ax 2 A Mathematics Topperlearning Com Tcz
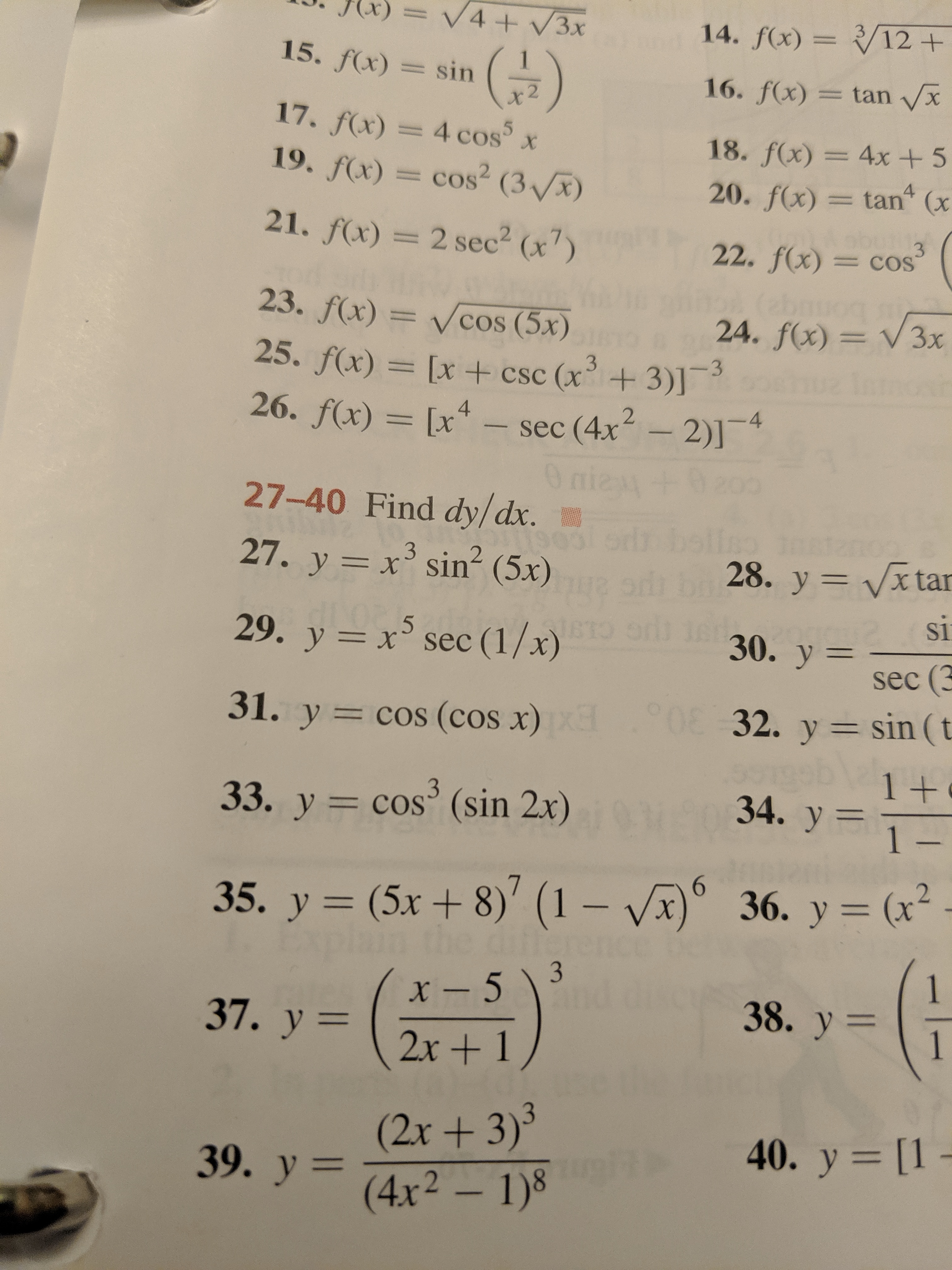



Answered V4 3x 14 F X 12 15 F X Sin 16 Bartleby
F(x) = function f'(x) = df(x) / dx = derivative of the function, slope of the function Ex f(x) = x^2 f(x)' = 2xSince `lim_ (x>c)f (x)=f (c)` f is continuous at all positive real numbers Therefore, f is continuous function We will now show that f (x)=x3,x in R is not differentiable at x = 3 `lim_ (h>0^) (f (3h)f (3))/h=lim_ (h>0^) (3h333)/h=lim_ (h>0^) (h0)/h=lim_ (h>0^)h/h=1`The inverse function is the reverse function of any given function Step to find the inverse function First, f(x) f ( x) with y y Interchange the variable After this, solve the new equation




1 F X X 3 Que Valores Puede Tomar La Variable X Que Valores Puede Tomar La Variable Y 2 Brainly Lat



Bellwork Graph Each Line 1 3x Y 6 2 Y 1 2 X 3 Y Ppt Video Online Download
Jan 28, · Consider the function f A → B defined by f (x) = ((x − 2)/(x − 3)) Is f oneone and onto?Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area We review their contentJul 03, 17 · See below f(x) = (1/3)^x 3 Before we start plotting points, let's first get an idea of some of the characterics of f(x) lim_(x>oo) f(x) = 0 3 = 3 We should note that f(x) > 3 very rapidly Ie We wont need very many points x>0 lim_(x>oo) f(x) = lim_(x>oo) 3^x3 = oo Again f(x) > oo quite rapidly f(0) = (1/3)^0 3 = 13 =2 So, (0, 2) is a point on our graph f(x) =0 > (1/3)^x




How Do You Find The Derivative Of F X 3 X 2 Using The Limit Definition Socratic




Evaluate Functions For X Given F X 3 Youtube
Shifting of Graph Suppose a function is {eq}y=f(x) {/eq};Click here to see ALL problems on Functions Question f (x)= x^33x^29x5 find and classify all stationary points sketch the graph of fx Answer by robertb (5567) ( Show Source ) You can put this solution on YOUR website!11 Find roots (zeroes) of F(x) = x 35x1 Polynomial Roots Calculator is a set of methods aimed at finding values of x for which F(x)=0 Rational Roots Test is one of the above mentioned tools It would only find Rational Roots that is numbers x which can be expressed as




Let F X X 3 X 1 And Let G X Be Its Inverse Function Then Equ




If F X X3 1 X3 Prove That F X F 1 X 0 Brainly In
Given f (x) = 3x 2 – x 4, find the simplified form of the following expression, and evaluate at h = 0 This isn't really a functionsoperations question, but something like this often arises in the functionsoperations context This looks much worse thanWe can shift the graph in the vertical and horizontal directions by adding and subtracting the constants, depending on the given conditionSolution for f (x)=x^31 equation Simplifying f (x) = x 3 1 Multiply f * x fx = x 3 1 Reorder the terms fx = 1 x 3 Solving fx = 1 x 3 Solving for variable 'f' Move all terms containing f to the left, all other terms to the right




Given That F X 2 X 4 And G X 3 X 5 Find Gf 3 With Noob Like Steps Please I Need A Really Clear Working To Fully Understand Thanks 3 Socratic



Transformations Of Functions College Algebra
Free functions calculator explore function domain, range, intercepts, extreme points and asymptotes stepbystepIf F(x)=x has no real solution then also F(F(x)=x has no real solutionHence, the name "piecewise" function When I evaluate it at various x values, I have to be careful to plug the argument into the correct piece of the function
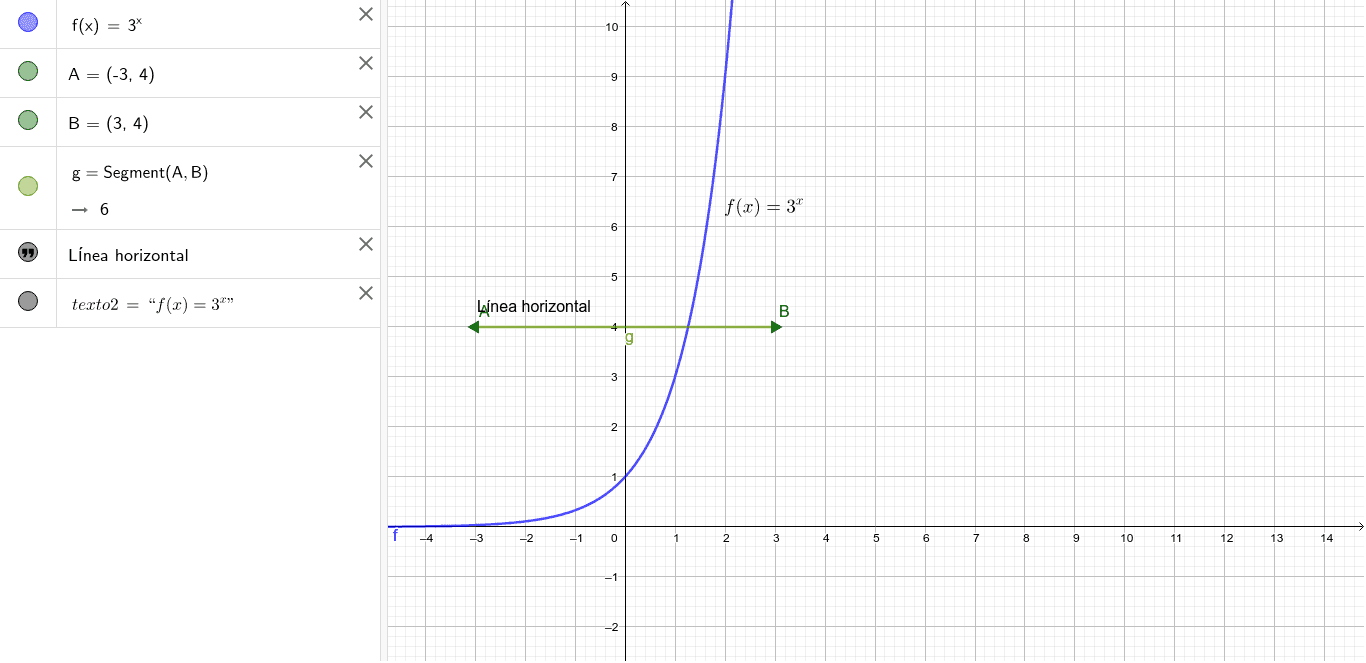



Funciones F X 3 X Geogebra
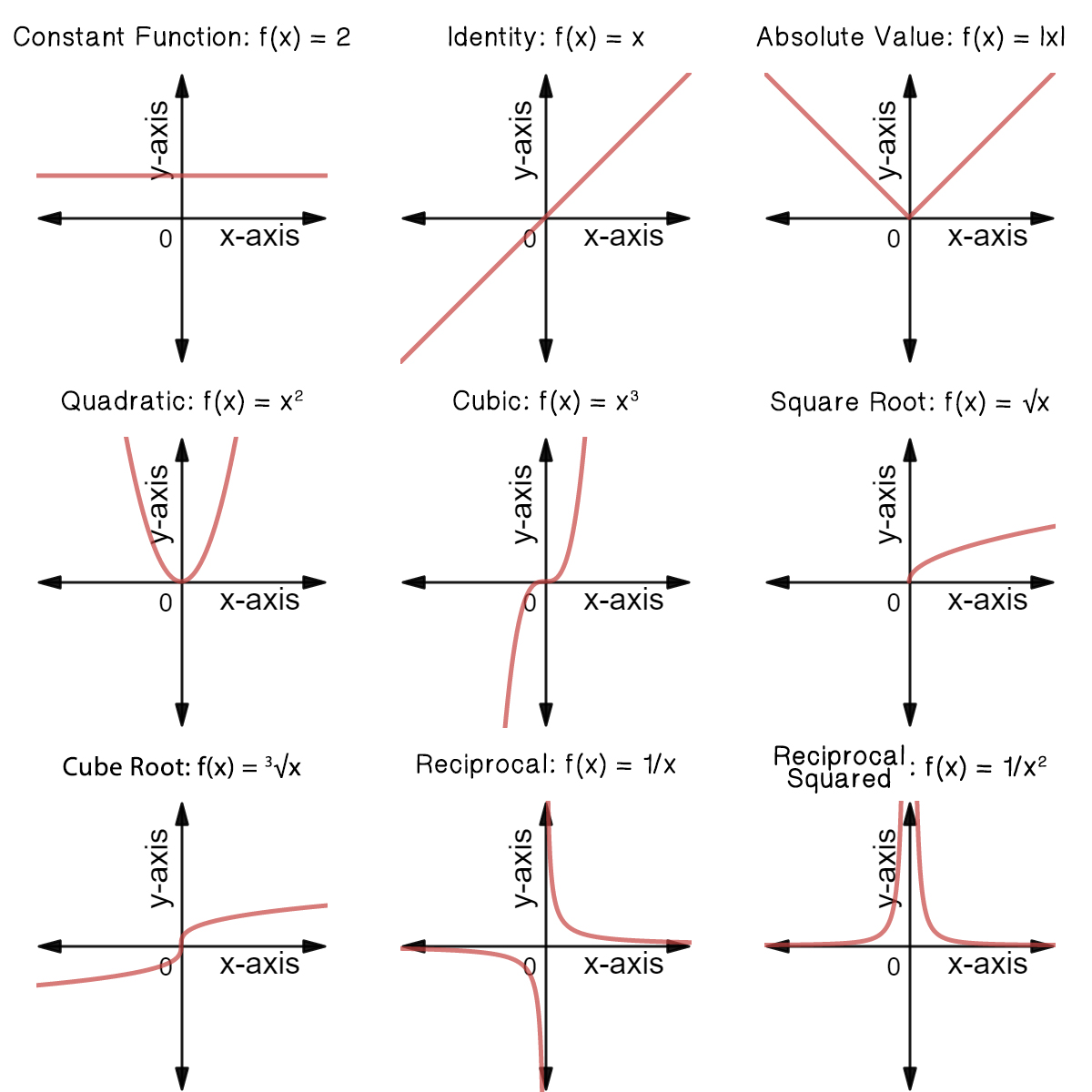



Classifying Common Functions Expii
Get an answer for 'f(x) = (x3)/(x1) find f'(0) f(x) = (x3)/(x1) find f'(0)' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesF (x) = (x1) (x2) (x3) , x ∈ 0,4, ∴ f (x) = x 3 6x 2 11x 6 As f (x) is a polynomial in x (1) f (x) is continuous on 0, 4 (2) f (x) is differentiable on (0, 4) Thus, all the conditions of LMVT are satisfied To verify LMVT we have to find c ∈ (0,4) such thatMar 10, 21 · Ex 51, 7 Find all points of discontinuity of f, where f is defined by 𝑓(𝑥)={ (𝑥3, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥≤−3@ −2𝑥, 𝑖𝑓−3




اسئلة محلولة عن الدوال والنهايات



Solved 1 Find The Inverse Of The Function F X 3 5 Poi Chegg Com
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge and




1 Solve 2x 3 4x 2 6x 0 Check With Gut 2 Solve Algebraically Or Graphically X 2 2x 15 Ppt Download




Maclaurin Series For F X 1 1 X 3 Math Calculus Showme




3 Hallar La Funcion Inversa Y Su Grafica F X X 2 Youtube
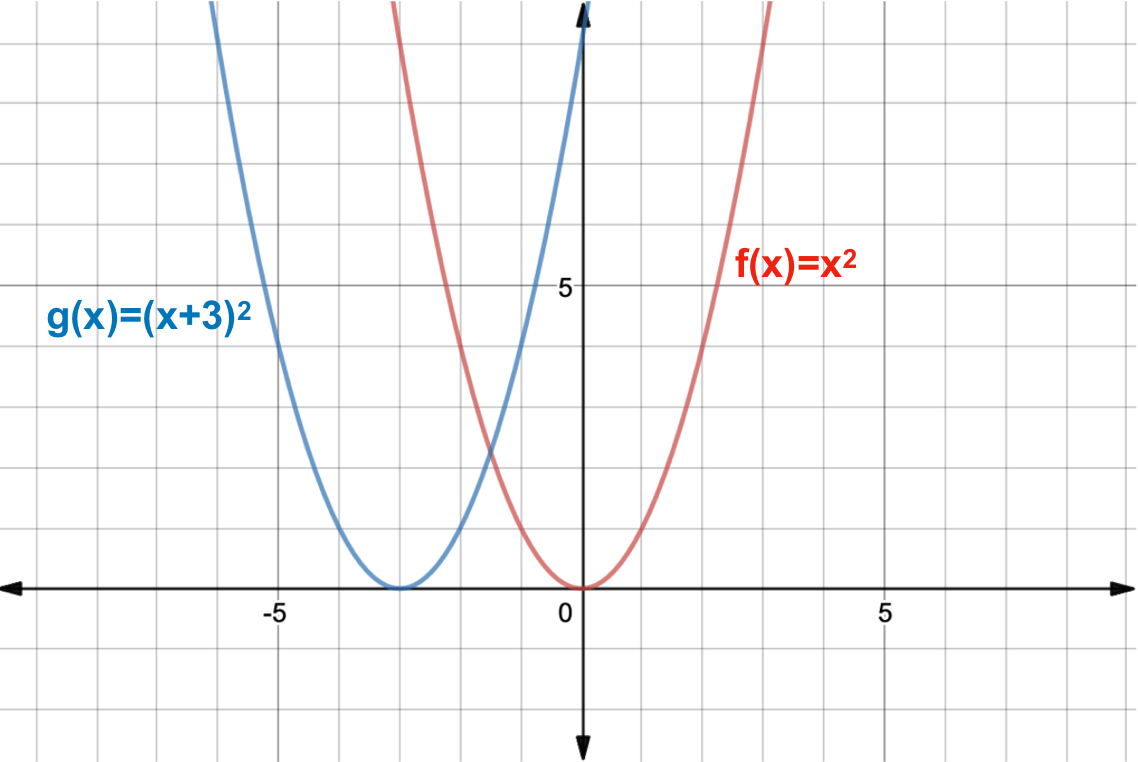



What Is A Function Transformation Expii




F X X 3 6 Geogebra
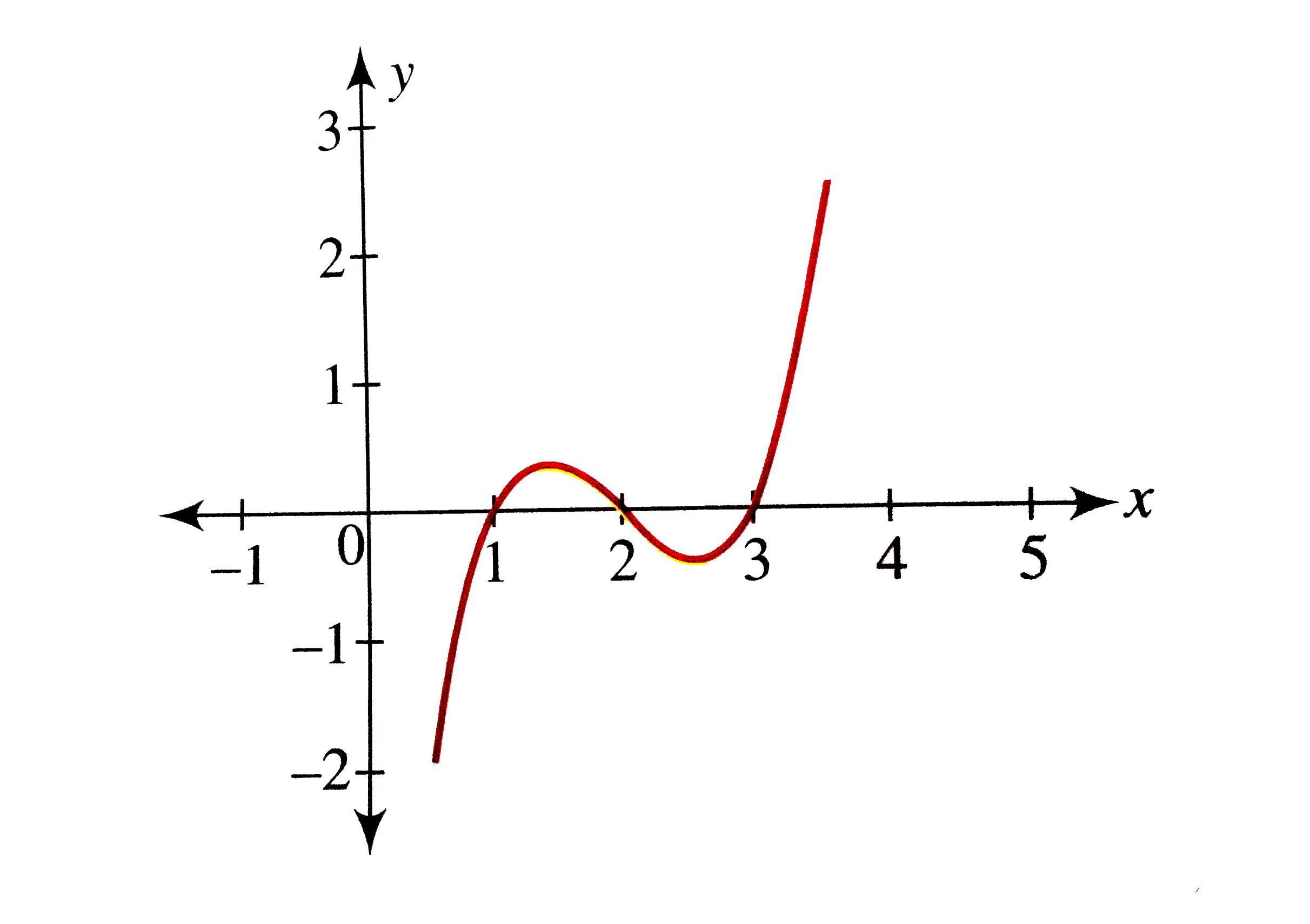



Draw The Graph Of F X X 1 X 2 X 3
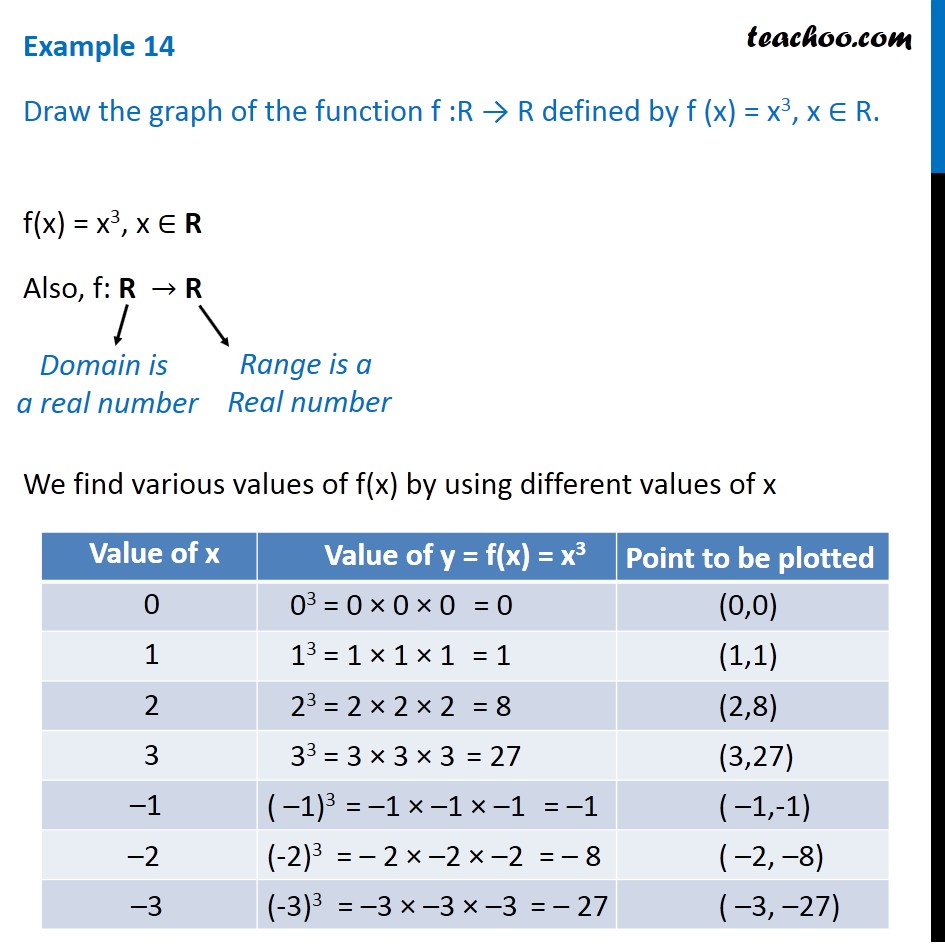



Example 14 Draw Graph Of F X X 3 Chapter 2 Class 11




Domain And Range Of F X X 3 X 3 Are Respectively




Grafica De F X 1 3x 2 1 X 3 3 Youtube




Find The Greatest Common Divisor Of F X 2x 3 2x 2 X 4 And G X X 4 3x 3 4x 2 3x Mathematics Stack Exchange




F X X 3 3 1 Zonealarm Results




Ex 1 3 13 F X 3 X3 1 3 Then Fof X Is A X1 3
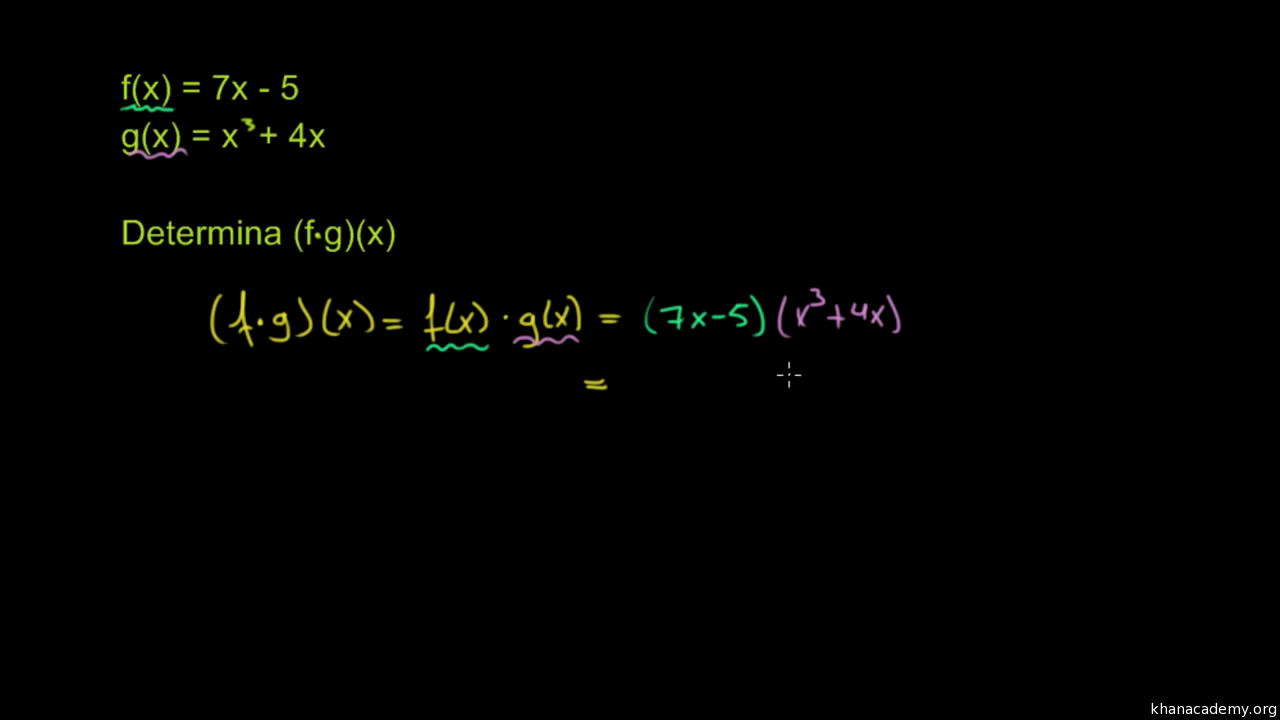



Multiplicar Funciones Video Funciones Khan Academy




Verifying Inverse Functions By Composition Not Inverse Video Khan Academy




Lista 3 Derivadas Practica Sobre Diversos Temas De Calculo I Contiene Ejercicios De Todo Tipo Studocu




Find The Equation X 3 5x 7 0 Which Lies Between 2 And 3 By The Method Of False Position Solution Mathematics 3 M3 Notes Question Answer Collection




Solution Given F X X 3 X 4 4 When F X Is Divided By X K The Remainder Is K Find K




Problem 1 Find The Critical Points Of The Function F X Y X3 6xy




Show That F R R Defined As F X X 3 Is Bijection Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com
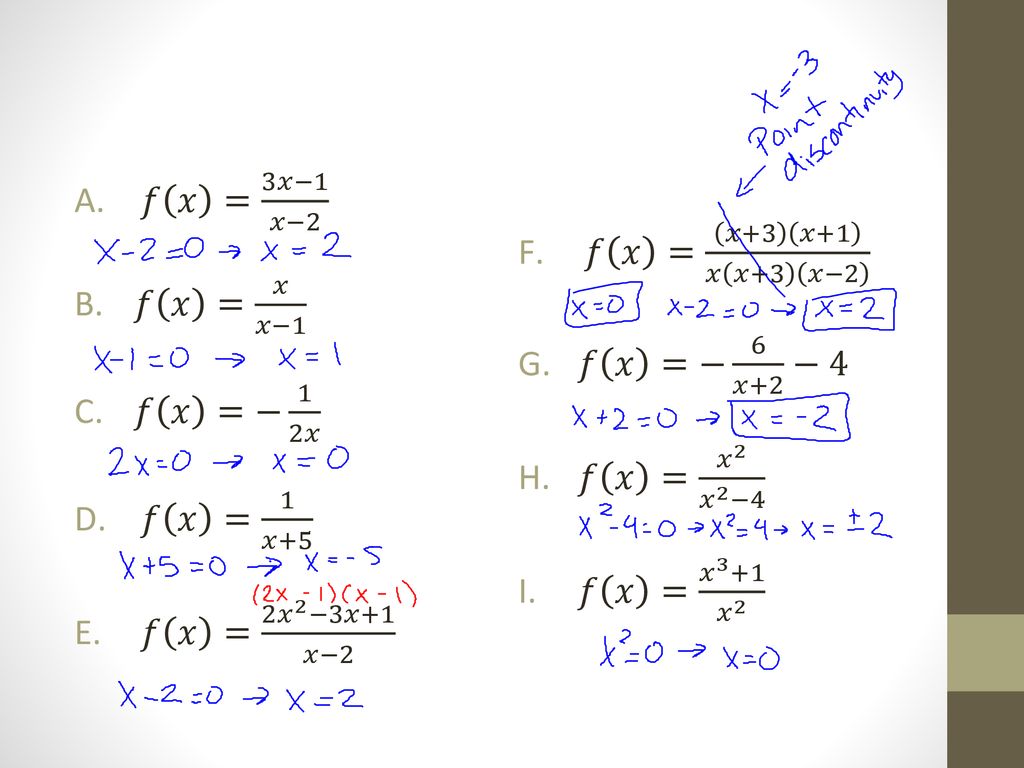



3 7 Graph Of Rational Functions Ppt Download




9 Polynomials Example 1 The Expression A X X 3 4x 2 7x 11 Is A Polynomial In X The Coefficients Of A X Are The Numbers 1 4 7 Pdf Free Download




Taller Funciones Limites Y Continuidad Numero Real Funcion Matematicas



Answer In Algebra For Dani Wagas




Construccion De La Funcion F X 3 4x Geogebra




1 F X X3 1 X F X X2 9 X F X X 3 X 2 X 3 X 1 F X 5 F X X 5 X F X X2 3 X 2 X 2 3 X Pdf Free Download




Dominio Y Rango De La Funcion F X 2 X 3 La Prof Lina M3 Youtube




2 2 The Graph Of A Function Mathematics Libretexts




Najti F 3 I F 1 Esli F X X 3 3 X 1 Shkolnye Znaniya Com




Answered 3 3x 1 34 F 33 F X 5x X2 36 Bartleby




Find The Divided Differences Of 𝑓 𝑥 𝑥3 𝑥 2 For The Argument 1 3 6 11 Wegglab




Answered For Problems 29 31 Use The Given Graph Bartleby




A Function F Is Defined By F X 3 2x Find X Such That F X F X Brainly In



Let F R To R Be A Function Defined By F X Max X X 3




Example 8 Find Derivative Of F X 3 At X 0 X 3 Examples



Solved 1 Find The Inverse Of The Function F X 3 5 Poi Chegg Com




Let F X 3 X 2 4 X 3 5 X 4 Then F X 0 Has A Exactly




Answered Express The Function In The Form F G 1 Bartleby




One To One Functions And Their Inverses Read Calculus Ck 12 Foundation




If F X 1 X X 3 X 3 Then F 5 Must Be Equal To




Calameo Funciones
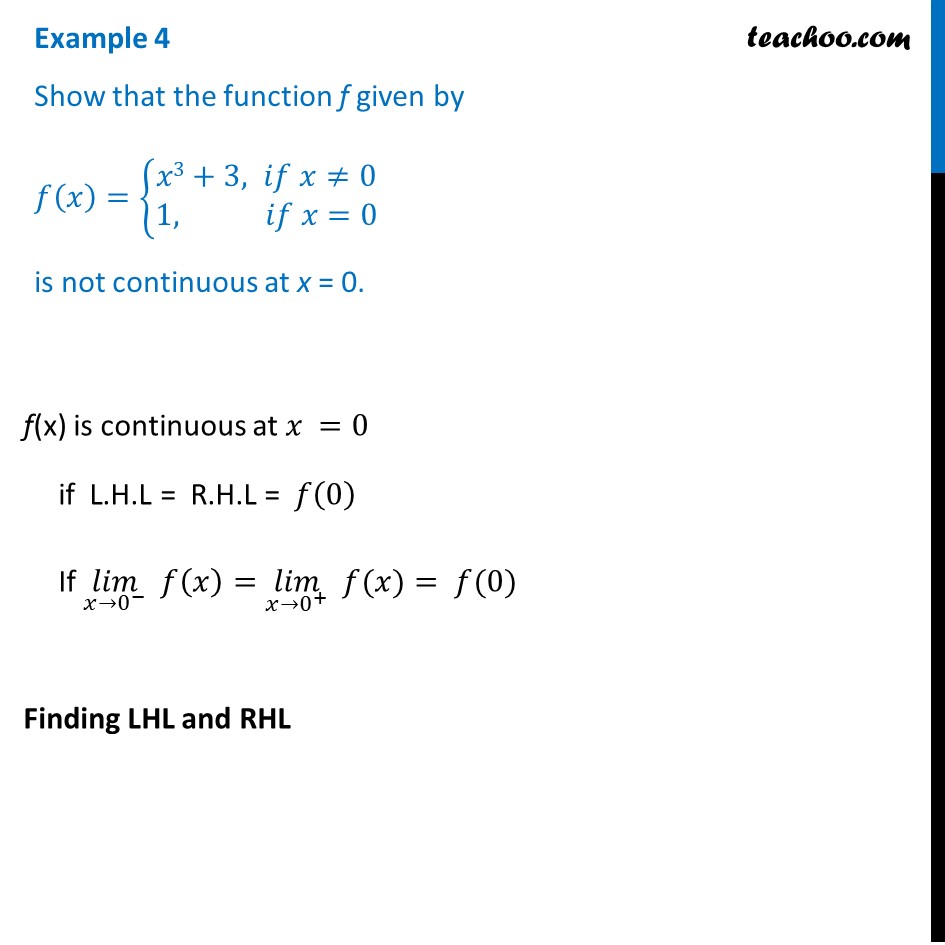



Example 4 Show F X X3 3 1 Is Not Continuous At X 0




Function F R R F X X 3 X Is




Para La Funcion F X X X X 3 A Graficar B Como Se Comporta La Funcion Brainly Lat




Solved 1 Find The Inverse Of The Function F X 3 5 Poi Chegg Com



Solved Find And Classify All The Critical Points Of Function F X Y X 3 Y 3 8xy Course Hero




Maximum Value Of Function F X Frac X 4 X 2 X 6 2x 3 1 When X 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Ex 1 3 4 If F X 4x 3 6x 4 Show That Fof X X




3a Grafica De La Funcion Valor Absoluto F X X 3 Youtube




Finding Values Of Derivative Given F Graph Mathematics Stack Exchange



How Do You Sketch The Graph F X X 3 1 Socratic



F X X2 4x 3 Para X 0 4 Geogebra
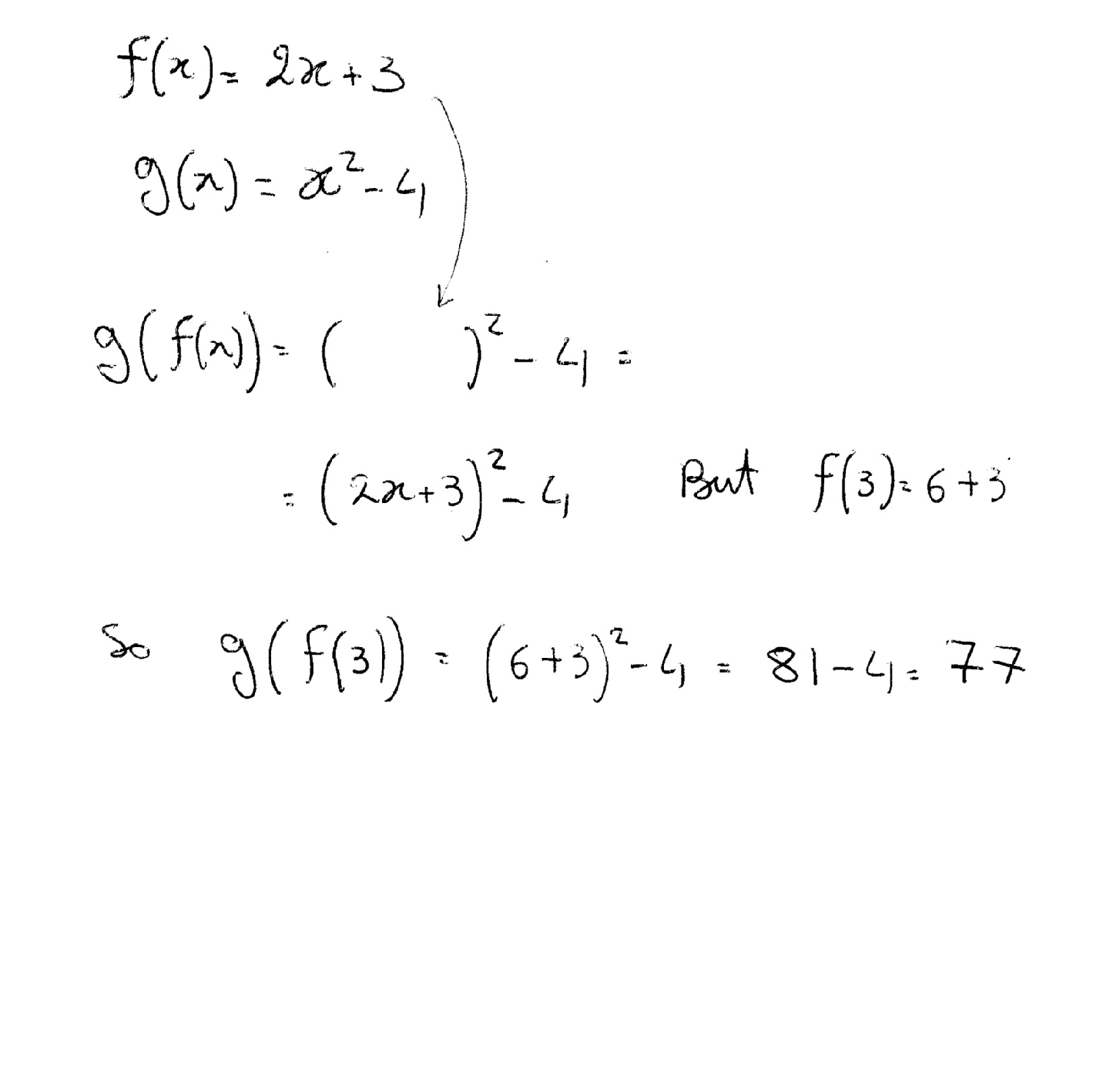



Let F X 2x 3 And G X X 2 4 And H X X 3 2 How Do You Find G F 3 Socratic




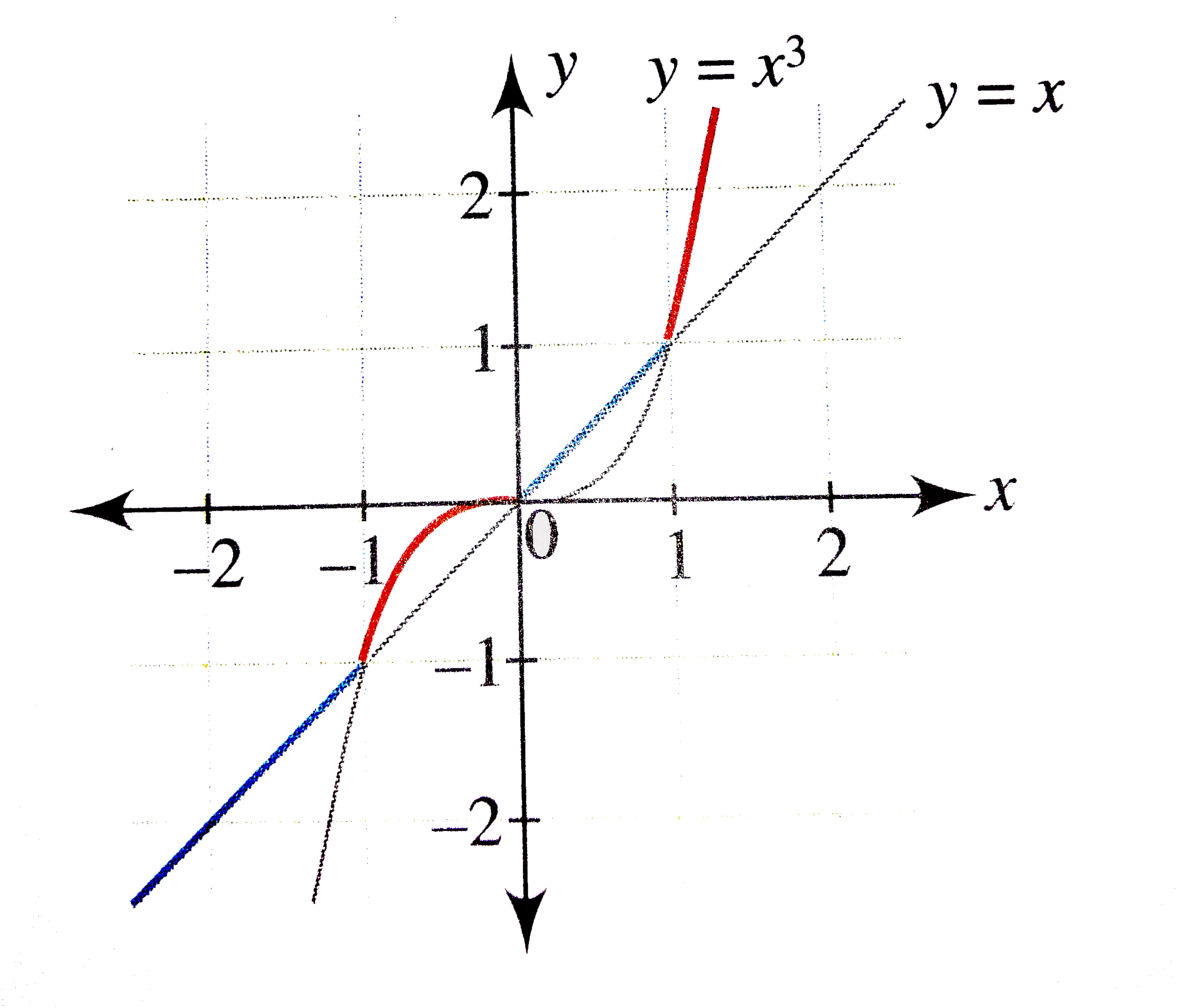
Consider The Function F X X 3 Draw The Graph Of F X Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com




Evaluate The Function For The Given Value Of X F X Chegg Com




F X 3 X Geogebra




If F X X 3 1x 3 Show That F X F 1x 0




El Limite De La Funcion F X 2x 3x 9 X 3 Cuando X Tiende A 3 Es Brainly Lat




Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 11 Chapter 3 Functions Download Free Pdf
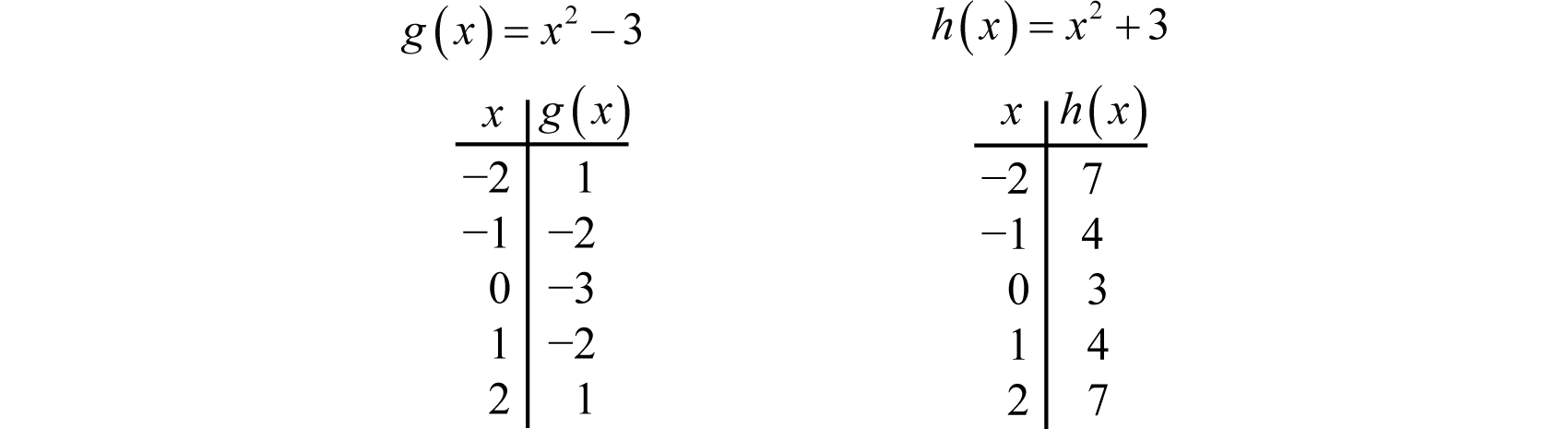



Using Transformations To Graph Functions
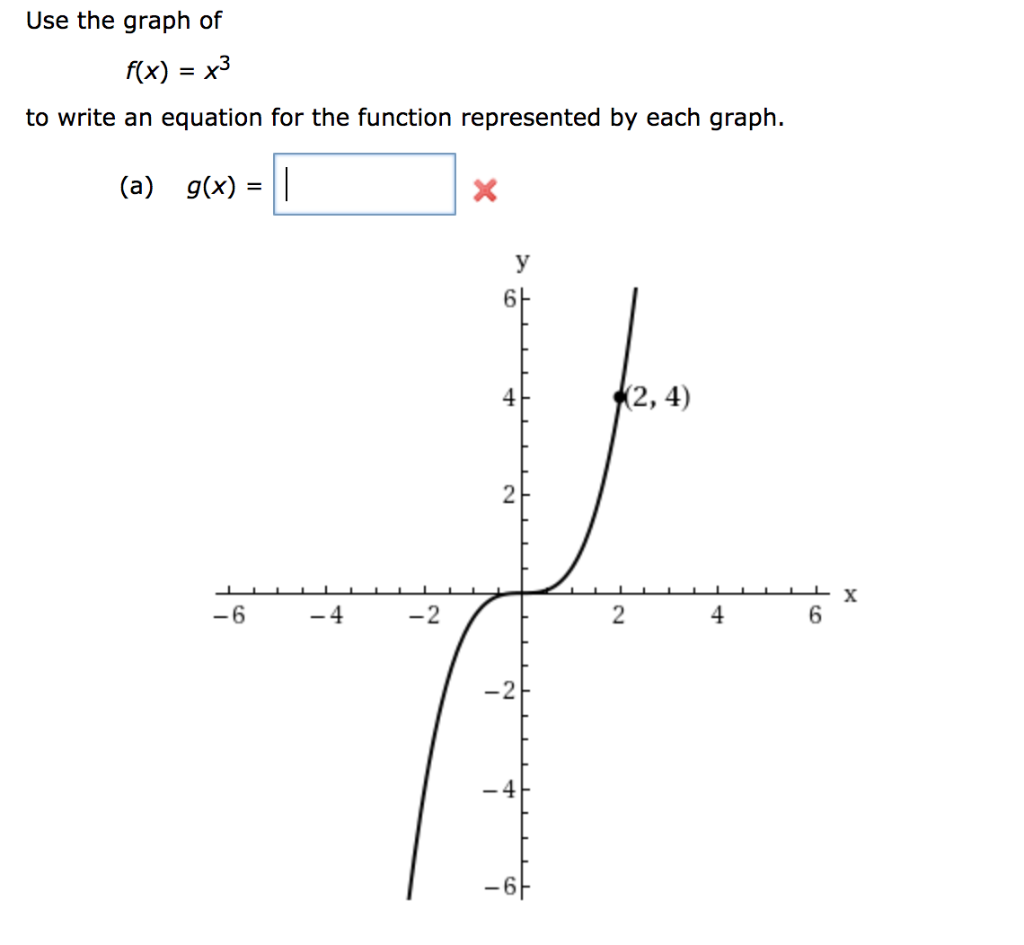



Solved Use The Graph Of F X X3 Equation For The Func Chegg Com


